Difference between revisions of "Sustainability Methods:About"
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
== About this wiki == | == About this wiki == | ||
| − | The aim of the ''Sustainability Methods Wiki'' is to '''present and explain diverse methods, terms and tools''' relevant to (Sustainability) Science and discuss underlying questions. It shall serve as '''a resource for students, researchers, teachers and any interested readers''' | + | The aim of the ''Sustainability Methods Wiki'' is to '''present and explain diverse scientific methods, terms and tools''' relevant to (Sustainability) Science and discuss underlying questions. It shall serve as '''a resource for students, researchers, teachers and any interested readers''' and tries to bridge the gap on how we approximate empirical knowledge, and how we ought to act based on this. Through an inclusive, reflexive and critical approach to the methodological canons, we try to contribute to solve the disciplinary slumber that defines much of modern science. |
=== Sub-Wikis === | === Sub-Wikis === | ||
'''The Wiki is divided in four different sub-wikis:''' | '''The Wiki is divided in four different sub-wikis:''' | ||
| − | * [[Courses]], which includes | + | * [[Courses]], which includes Wiki entries that parallel university courses, and in the future also stand-alone courses on specific topics. |
| − | * [[Methods]], where a range of scientific methods are presented and | + | * [[Methods]], where a range of scientific methods are presented and discussed that are crucial for Sustainability Science, and many more branches of science. |
* [[Skills & Tools]], which lists helpful team and individual skills as well as tools that facilitate scientific and non-scientific work. | * [[Skills & Tools]], which lists helpful team and individual skills as well as tools that facilitate scientific and non-scientific work. | ||
| − | * [[Normativity of Methods]], which revolves around questions of Normativity in Science. | + | * [[Normativity of Methods]], which revolves around questions of Normativity in Science, and how science relates to the 'real world'. |
=== The Method Recommendation Tool === | === The Method Recommendation Tool === | ||
| − | The Method Recommendation Tool (MRT) is designed to broaden your perspective on scientific methods. You select three scientific methods that you like and that you are familiar with. Based on their underlying Design Criteria (see below), the MRT creates a profile and then recommends five other scientific methods for each method that share traits with the selected ones, highlighting what you might be interested in. You can then read about these methods on the Wiki and broaden and / or sharpen your methdological profile. | + | The Method Recommendation Tool (MRT) is a digital tool designed to broaden your perspective on scientific methods. You select three scientific methods that you like and that you are familiar with. Based on their underlying Design Criteria (see below), the MRT creates a profile and then recommends five other scientific methods for each method that share traits with the selected ones, highlighting what you might be interested in. You can then read about these methods on the Wiki and broaden and / or sharpen your methdological profile. |
=== Design Criteria of Methods === | === Design Criteria of Methods === | ||
| − | At the core of the Method entries on the Wiki lie the Design Criteria of Scientific Methods. If you want to read more about the idea behind it, please refer to the [[Design Criteria of Methods]] entry. In short, the idea is to challenge the prevalent assumption that each scientific discipline must be restricted to a narrow set of scientific methods. Instead, the Wiki suggests that methods should be selected according to the intended type of created knowledge. To show that methods are not bound to disciplines, '''the Wiki categorizes every | + | At the core of the Method entries on the Wiki lie the Design Criteria of Scientific Methods. If you want to read more about the idea behind it, please refer to the [[Design Criteria of Methods]] entry. In short, the idea is to challenge the prevalent assumption that each scientific discipline must be restricted to a narrow set of scientific methods. Instead, the Wiki suggests that methods should be selected according to the intended type of created knowledge. To show that methods are not bound to disciplines, '''the Wiki categorizes every presented scientific method according to four different design criteria:''' |
<br/> | <br/> | ||
* [[:Category:Quantitative|Quantitative]] - [[:Category:Qualitative|Qualitative]] | * [[:Category:Quantitative|Quantitative]] - [[:Category:Qualitative|Qualitative]] | ||
Revision as of 07:20, 29 April 2021
About this wiki
The aim of the Sustainability Methods Wiki is to present and explain diverse scientific methods, terms and tools relevant to (Sustainability) Science and discuss underlying questions. It shall serve as a resource for students, researchers, teachers and any interested readers and tries to bridge the gap on how we approximate empirical knowledge, and how we ought to act based on this. Through an inclusive, reflexive and critical approach to the methodological canons, we try to contribute to solve the disciplinary slumber that defines much of modern science.
Sub-Wikis
The Wiki is divided in four different sub-wikis:
- Courses, which includes Wiki entries that parallel university courses, and in the future also stand-alone courses on specific topics.
- Methods, where a range of scientific methods are presented and discussed that are crucial for Sustainability Science, and many more branches of science.
- Skills & Tools, which lists helpful team and individual skills as well as tools that facilitate scientific and non-scientific work.
- Normativity of Methods, which revolves around questions of Normativity in Science, and how science relates to the 'real world'.
The Method Recommendation Tool
The Method Recommendation Tool (MRT) is a digital tool designed to broaden your perspective on scientific methods. You select three scientific methods that you like and that you are familiar with. Based on their underlying Design Criteria (see below), the MRT creates a profile and then recommends five other scientific methods for each method that share traits with the selected ones, highlighting what you might be interested in. You can then read about these methods on the Wiki and broaden and / or sharpen your methdological profile.
Design Criteria of Methods
At the core of the Method entries on the Wiki lie the Design Criteria of Scientific Methods. If you want to read more about the idea behind it, please refer to the Design Criteria of Methods entry. In short, the idea is to challenge the prevalent assumption that each scientific discipline must be restricted to a narrow set of scientific methods. Instead, the Wiki suggests that methods should be selected according to the intended type of created knowledge. To show that methods are not bound to disciplines, the Wiki categorizes every presented scientific method according to four different design criteria:
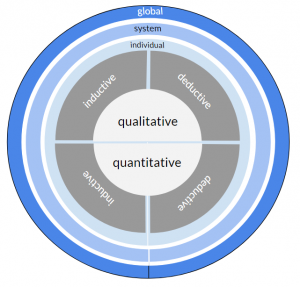
- Quantitative - Qualitative
- Inductive - Deductive
- Spatial scale: Individual - System - Global
- Temporal scale: Past - Present - Future
You can click on each category for more information and all the entries that belong to this category.
Each method fulfills one or more categories per design criterion. To highlight this, each method entry includes a visualisation of the method's categorization. The general visualisation is designed as follows:
This visualisation above refers to the majority of methods that focus on a slice of time - the present.
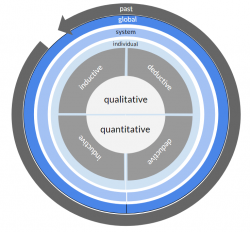
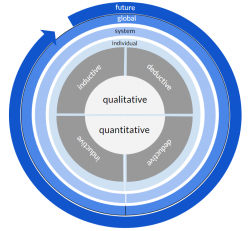
However, a range of methods exists that enable the researchers to investigate the past or the future. For these methods, the concept can be adapted to indicate a focus on the past (left) and a focus on the future (right) through one more circle.
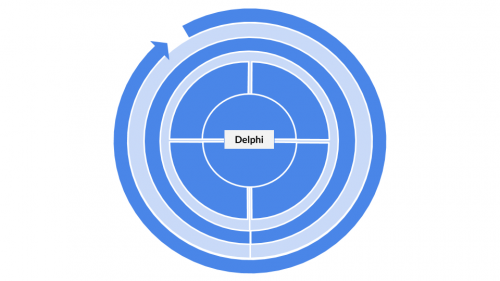
As an example, the Delphi method is both quantitative and qualitative, both inductive and deductive, looks at systems and into the future. The respective visualisation therefore looks like this:
The categorization may serve as a guide to understand how methods are connected and to select methods for one's own research. Every reader may browse through the presented methods and learn about methods that never seemed fitting for one's own research, but maybe are.