Difference between revisions of "Legal Research"
(Created page with "450px|frameless|left|[[Sustainability Methods:About|Method categorization for Legal Research]] <br/> {|class="wikitable" style="text-ali...") |
|||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
! colspan = 3 | Method categorization | ! colspan = 3 | Method categorization | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | [[:Category:Quantitative|Quantitative]] || colspan="2" | '''[[:Category:Qualitative|Qualitative]]''' |
|- | |- | ||
| '''[[:Category:Inductive|Inductive]]''' || colspan="2"| '''[[:Category:Deductive|Deductive]]''' | | '''[[:Category:Inductive|Inductive]]''' || colspan="2"| '''[[:Category:Deductive|Deductive]]''' | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
<br/>__NOTOC__ | <br/>__NOTOC__ | ||
| − | + | '''Annotation''': Due to the special role of Law as a scientific discipline, this entry will focus more on legal research as a whole as opposed to one specific method. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | == Background == | |
| − | + | The field of Law has a long-standing history. "Roman legal doctrine developed since the second century before Christ, and reached a very high level as from the third century after Christ. Its rediscovery and renewed study in Bologna in the eleventh century was the start for the creation of universities." (van Hoecke 2011, p.1). The emergence of Law and its eventual institutionalisation as a scientific discipline was fundamentally based on the reading and interpretation of (Roman) legal documents (2). "During the whole of the Middle-Ages, legal doctrine was highly thought of and considered as a 'scientific discipline', as in those times 'authoritative interpretation', not 'empirical research', was the main criterion for the scientific status of a discipline." (van Hoecke 2011, p.1). '''The discipline subsequently spread from the first universities in Italy throughout Europe''' (2). In this time, legal work was mostly restricted to each national context due to the differences in the respective legal systems (2). This early approach to Law as a scientific discipline represents the so-called 'doctrinal approach' which is still the most common understanding of legal work (see What the method does). | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | However, a second approach developed from the 17th Century on, but mainly from the 19th Century until today. With the rise of positivism - which implies that the only valid knowledge arises from scientific inquiry and falsification of scientific theory -, a new understanding of science emerged. Here, the use of empirical data, the testing of hypotheses and the development of theories, independent from geographical limitations, became the new scientific ideal. In consequence, Law as a scientific discipline changed (van Hoecke 2011, p.1). '''The research focus in Law partly shifted, both in terms of research questions and methodology''': "[i]n the 1960s and 1970s, legal realists and socio-legal scholars started the law and society movement, and pointed to the importance of understanding the gap between 'law in books' and 'law in action', and the operation of law in society. They were interested in examining the legal system in terms of whether legal reform brings about beneficial social effects and protects the interests of the public. Similarly, in the 1980s critical legal studies integrated ideas and methods found in disciplines such as sociology, anthropology and literary theory." (McConville & Chui 2007, p.5). With Law being a discipline between the Sciences and the Humanities, this new movement borrowed heavily from the Social Sciences in terms of methodology. New adjacent disciplines emerged, including legal sociology, legal psychology and law and economics, among others (2, 5). This 'Law in context' - also called 'socio-legal' - approach includes new topics and methodological directions with a stronger focus on empirical research and theory building and has been universally taken up in academic institutions. | |
| − | [ | + | |
| − | + | From this contextualized approach to Law, research emerged on the relationship between Law and Society and questions of power relations, more specificially on aspects such as gender, social class, ethnicity and religion (5). ''''Socio-legal research' may be seen as an alternative or a supplement, but not necessarily as a substitute to traditional legal analysis''' (2, 5). The openness towards a contextualization of Law acknowledges the fact that Law is influenced by thoughts and discourses from other disciplines such as sociology, economics, political science, history and psychology (4, 7). In addition, "understanding of the modern patent law, environmental law, and information technology law presupposes adequate study of biotechnology, ecology, and information technology." (4, p.18). New approaches to and combinations of methods have emerged and continue to develop. The common 'doctrinal' approach to legal research, i.e. collecting, reading and interpreting (legal) texts, is increasingly scrutinized as the primary methodological approach (2, 3). According to critics, legal publications and teaching in academic institutions do not sufficiently reflect upon the methodological approaches of traditional legal research (2, 5). This critique stems from a comparison to other established disciplines in the (Social) Sciences which have been using a diverse set of defined methodological approaches for decades (2). It has also emerged in view of fundamental changes in academia in the last decades, notably in terms of methodological advancements and trends of internationalisation (2). | |
| − | |||
Revision as of 11:36, 21 October 2020
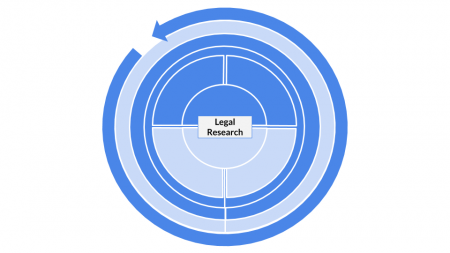
| Method categorization | ||
|---|---|---|
| Quantitative | Qualitative | |
| Inductive | Deductive | |
| Individual | System | Global |
| Past | Present | Future |
Annotation: Due to the special role of Law as a scientific discipline, this entry will focus more on legal research as a whole as opposed to one specific method.
Background
The field of Law has a long-standing history. "Roman legal doctrine developed since the second century before Christ, and reached a very high level as from the third century after Christ. Its rediscovery and renewed study in Bologna in the eleventh century was the start for the creation of universities." (van Hoecke 2011, p.1). The emergence of Law and its eventual institutionalisation as a scientific discipline was fundamentally based on the reading and interpretation of (Roman) legal documents (2). "During the whole of the Middle-Ages, legal doctrine was highly thought of and considered as a 'scientific discipline', as in those times 'authoritative interpretation', not 'empirical research', was the main criterion for the scientific status of a discipline." (van Hoecke 2011, p.1). The discipline subsequently spread from the first universities in Italy throughout Europe (2). In this time, legal work was mostly restricted to each national context due to the differences in the respective legal systems (2). This early approach to Law as a scientific discipline represents the so-called 'doctrinal approach' which is still the most common understanding of legal work (see What the method does).
However, a second approach developed from the 17th Century on, but mainly from the 19th Century until today. With the rise of positivism - which implies that the only valid knowledge arises from scientific inquiry and falsification of scientific theory -, a new understanding of science emerged. Here, the use of empirical data, the testing of hypotheses and the development of theories, independent from geographical limitations, became the new scientific ideal. In consequence, Law as a scientific discipline changed (van Hoecke 2011, p.1). The research focus in Law partly shifted, both in terms of research questions and methodology: "[i]n the 1960s and 1970s, legal realists and socio-legal scholars started the law and society movement, and pointed to the importance of understanding the gap between 'law in books' and 'law in action', and the operation of law in society. They were interested in examining the legal system in terms of whether legal reform brings about beneficial social effects and protects the interests of the public. Similarly, in the 1980s critical legal studies integrated ideas and methods found in disciplines such as sociology, anthropology and literary theory." (McConville & Chui 2007, p.5). With Law being a discipline between the Sciences and the Humanities, this new movement borrowed heavily from the Social Sciences in terms of methodology. New adjacent disciplines emerged, including legal sociology, legal psychology and law and economics, among others (2, 5). This 'Law in context' - also called 'socio-legal' - approach includes new topics and methodological directions with a stronger focus on empirical research and theory building and has been universally taken up in academic institutions.
From this contextualized approach to Law, research emerged on the relationship between Law and Society and questions of power relations, more specificially on aspects such as gender, social class, ethnicity and religion (5). 'Socio-legal research' may be seen as an alternative or a supplement, but not necessarily as a substitute to traditional legal analysis (2, 5). The openness towards a contextualization of Law acknowledges the fact that Law is influenced by thoughts and discourses from other disciplines such as sociology, economics, political science, history and psychology (4, 7). In addition, "understanding of the modern patent law, environmental law, and information technology law presupposes adequate study of biotechnology, ecology, and information technology." (4, p.18). New approaches to and combinations of methods have emerged and continue to develop. The common 'doctrinal' approach to legal research, i.e. collecting, reading and interpreting (legal) texts, is increasingly scrutinized as the primary methodological approach (2, 3). According to critics, legal publications and teaching in academic institutions do not sufficiently reflect upon the methodological approaches of traditional legal research (2, 5). This critique stems from a comparison to other established disciplines in the (Social) Sciences which have been using a diverse set of defined methodological approaches for decades (2). It has also emerged in view of fundamental changes in academia in the last decades, notably in terms of methodological advancements and trends of internationalisation (2).