Integrated Development Environments (IDE)
Still in Edition Mode
What is an IDE?
You have installed Python and its distribution or package manager, now what? The next important question is where are you going to write and run your Python code?
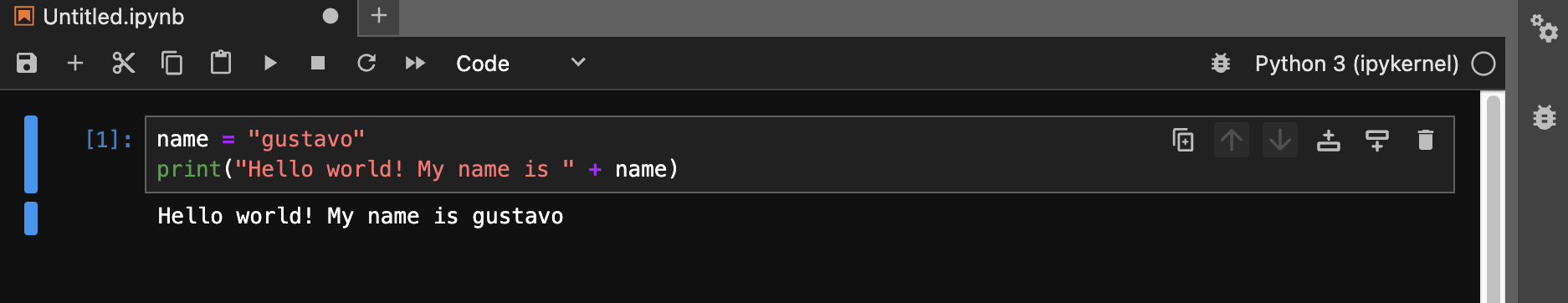
You can basically write Python code in any text editor applications such as Windows Notepad or macOS TextEdit, and then run it in your terminal command line (Windows Powershell or macOS terminal). For example, you can a create a very short python script:
name = "gustavo"
print("Hello world! My name is " + name)
You save the text file as “myscript.py” and then run it in the terminal as follows:
(base) user91@mycomputer ~ % python myscript.py Hello world! My name is Gustavo
However, in very few exceptions people run python in this way. Normally, what is used is a Integrated Development Environment (IDE). These IDEs are applications where you can write and run Python code in an easier and more comfortable way. For example, this is the same python code but run in a Jupyter Notebook:
The difference between both are noticeable. Coding in an IDE provides several advantages or functionalities, for example, the text color. In the above Jupyter Notebook example, you can see that the variable name is in white, the string value is in red, the function print() is in green. This allows you to better identify the several components of your code. In this sense, working in an IDE helps you to better understand and read your code, and track errors. Depending on the IDE, you get different functionalities such as autocompletion, file management, version control, automation tools, visualization, etc.
Among the most popular IDEs are JupyterLab (which contains Jupyter Notebooks), Visual Studio, RStudio Code and PyCharm, however the latter is more dedicated for python web development. It is recommended to first try IDEs that are free of cost such as JupyterLab and Visual Studio Code, and select the one that works best for you. Important about these IDEs is that you don’t need necessarily internet connection to run them or to work with them. Check this entry to know more about the logic of coding in notebooks.
Anaconda distribution contains several free and paid IDEs that you can try out right awat. If you don’t want to use an IDE for now, you can also use a web application called “Google Colab”, which offers a development environment in the notebooks format. If your computer is not powerful enough for some data science tasks, you can use Google Colab and either use it for free and pay for extra computational power if needed (for example purchasing some GPU's). However, you need a stable internet connection for this. Check this entry to get started with Google Colab.
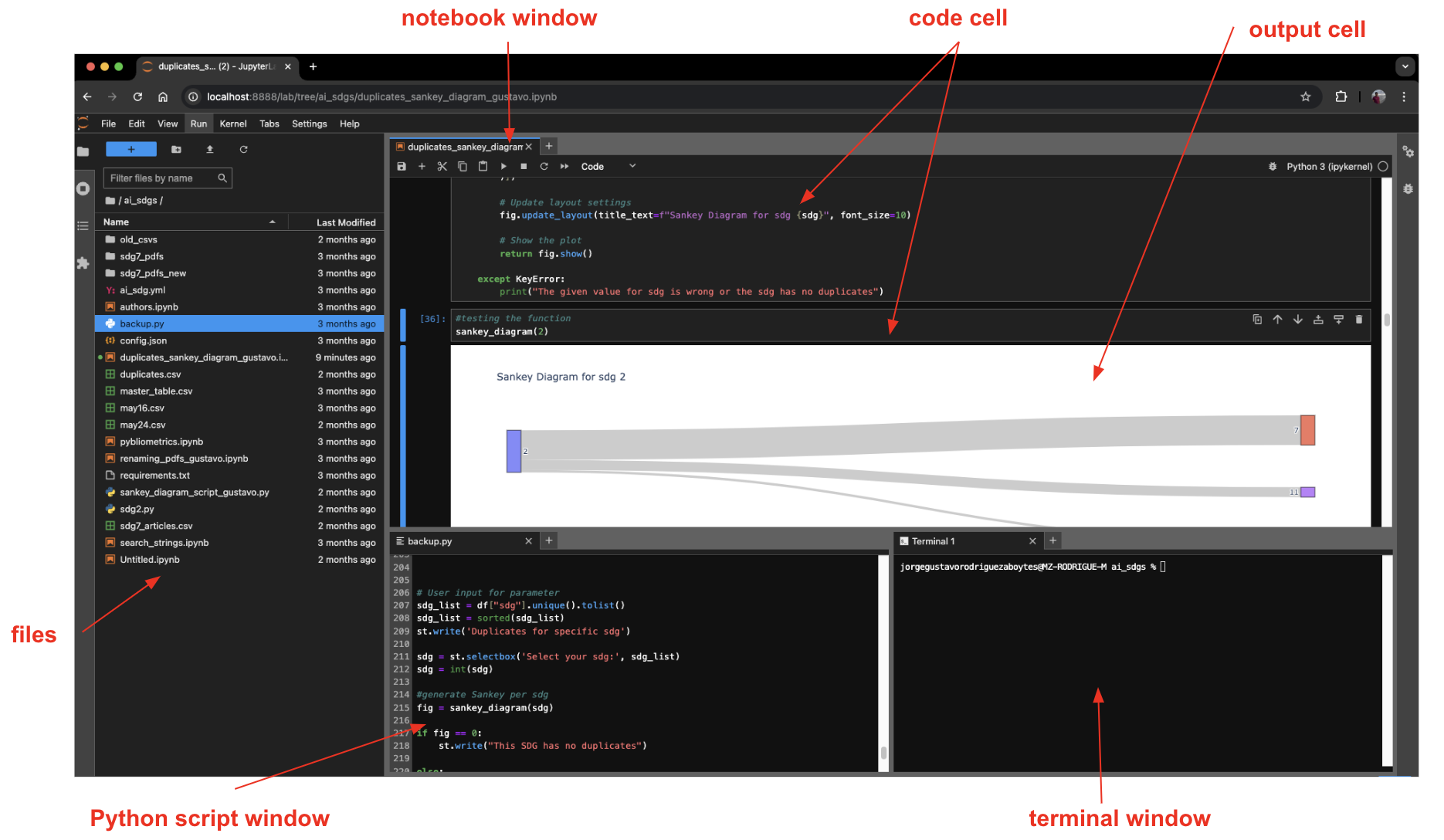
JupyterLab
JupyterLab is an evolution of a Jupyter Notebook, which is a coding environment where you can combine text/markdown cells with code cells. Jupyter Lab not only allows you to work with Jupyter Notebooks, but also with conventional python scripts, text and markdown files. Moreover you have
Visual Studio Code
Visual Studio Code
Other IDEs
Pycharm is a