Principal Component Analysis
Contents
Introduction & Motivation
You are a huge pizza lover. I mean, who doesn't like pizza (I passionately enjoy pizza Hawaii, change my mind!). You are also a data enthusiast. Then you stumbled on this dataset, which contains a lot of nutrient measurements in various pizzas from different pizza brands.
- brand -- Pizza brand (class label)
- id -- Sample analysed
- mois -- Amount of water per 100 grams in the sample
- prot -- Amount of protein per 100 grams in the sample
- fat -- Amount of fat per 100 grams in the sample
- ash -- Amount of ash per 100 grams in the sample
- sodium -- Amount of sodium per 100 grams in the sample
- carb -- Amount of carbohydrates per 100 grams in the sample
- cal -- Amount of calories per 100 grams in the sample
How can you represent this data as concise and understandable as possible? It is impossible to plot all variables as is onto a flat screen/paper.
Curse of dimensionality
This term was coined by Richard R. Bellman, an American applied mathematician. As the number of features / dimensions increases, the distance among data points grows exponential. Things become really sparse as the instances lie very far away from each other. This makes applying machine learning methods much more difficult, since there is a certain relationship between the number of features and the number of training data. In short, with higher dimensions you need to gather much more data for learning to actually occur, which leaves a lot of room for error. Moreover, higher-dimension spaces have many counter-intuitive properties, and the human mind, as well as most data analysis tools, is used to dealing with only up to three dimensions (like the world we are living in). Thus, data visualization and intepretation become much harder, and computational costs of model training greatly increases.
Principle Component Analysis
Principle component analysis is one of the foundational methods to combat the curse of dimensionality. It is an unsupervised learning algorithm whose goals is to reduce the dimensionality of the data, condensing its entirety down to a low number of dimensions (also called principle components, usually two or three).
Although it comes with a cost of losing some information, it makes data visualization much easier, improves the space and time complexity required for machine learning algorithms tremendously, and allows for more intuitive intepretation of these models. PCA can also be categorized a feature extraction techniques, since it creates these principle components - new and more relevant features - from the original ones.
The essence of PCA lies in finding all directions in which the data "spreads", determining the extent in which the data spreads in those directions, keeping only few direction in which the data spreads the most. And voila, these are your new dimensions / features of the data.
Road to PCA
Standardization
Oftentimes the features in the data are measured on different scales. This step makes sure that all features contribute equally to the analysis. Otherwise, variables with large range will trump thoses with smaller range (for example: a time variable that ranges between 0ms and 1000ms with dominate over a distance variable that ranges between 0m and 10m). Each variable can be scaled by subtracting its mean and dividing by the standard deviation (this is the same as calculating the z-score, and in the end, all variables with have the same mean 0 and standard deviation of 1).
Covariance matrix
The covariance matrix is a square d x d matrix, where each entry represents the covariance of a possible pair of the original features. It has the following properties:
- The size of the matrix is equal to the number of features in the data
- The main diagonal on the matrix contains the variances of each initial variables.
- The matrix is symmetric, since Cov(d1, d2) = Cov(d1, d2)
The covariance matrix gives you a summary of the relationship among the initial variables.
- A positive value indicate a directly proportional relationship (as d1 increases, d2 increases, and vice versa)
- A negative value indicate a indirectly proportional relationship (as d1 increases, d2 decreases, and vice versa)
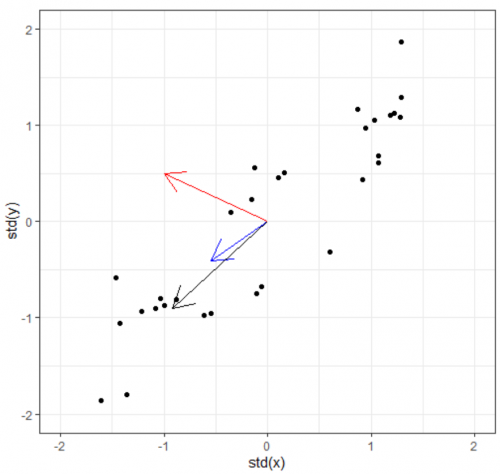
Eigenvectors / Principle Components & Eigenvalues
Now we have the covariance matrix. This matrix can be used to transform one vector into another. Normally when this transformation happens, two things happen: the original is rotated and get streched/squished to form a new vector. When an abitrary vector is multipled by the covariance matrix, the result will be a new vector whose direction is nudged/rotated towards the greatest spread in the data. In the figure below, we start with the arbitrary vector (-1, 0.5) in red. Multiplying the red vector with covariance matrix gives us the blue vector, and repeating this gives us the black vector. As you can see, the result rotation tends to converge towards the widest spread direction of the data.