Difference between revisions of "Integrated Development Environments (IDE)"
| (6 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Still in Edition Mode''' | '''Still in Edition Mode''' | ||
| − | == | + | == What is an IDE? == |
You have installed Python and its distribution or package manager, now what? The next important question is where are you going to write and run your Python code? | You have installed Python and its distribution or package manager, now what? The next important question is where are you going to write and run your Python code? | ||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
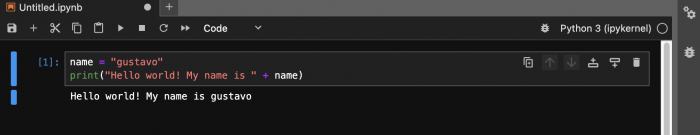
However, in very few exceptions people run python in this way. Normally, what is used is a Integrated Development Environment (IDE). These IDEs are applications where you can write and run Python code in an easier and more comfortable way. For example, this is the same python code but run in a Jupyter Notebook: | However, in very few exceptions people run python in this way. Normally, what is used is a Integrated Development Environment (IDE). These IDEs are applications where you can write and run Python code in an easier and more comfortable way. For example, this is the same python code but run in a Jupyter Notebook: | ||
| − | [[File:Example of an IDE.png| | + | [[File:Example of an IDE.png|700px|thumbnail|center|Example of an IDE (JupyterLab) looks like. Source: own]] |
The difference between both are noticeable. Coding in an IDE provides several advantages or functionalities, for example, the text color. In the above Jupyter Notebook example, you can see that the variable name is in white, the string value is in red, the function print() is in green. This allows you to better identify the several components of your code. In this sense, working in an IDE helps you to better understand and read your code, and track errors. Depending on the IDE, you get different functionalities such as autocompletion, file management, version control, automation tools, visualization, etc. | The difference between both are noticeable. Coding in an IDE provides several advantages or functionalities, for example, the text color. In the above Jupyter Notebook example, you can see that the variable name is in white, the string value is in red, the function print() is in green. This allows you to better identify the several components of your code. In this sense, working in an IDE helps you to better understand and read your code, and track errors. Depending on the IDE, you get different functionalities such as autocompletion, file management, version control, automation tools, visualization, etc. | ||
| − | Among the most popular | + | Among the most popular IDEs are JupyterLab (which contains Jupyter Notebooks), Visual Studio, RStudio Code and PyCharm, however the latter is more dedicated for python web development. It is recommended to first try IDEs that are free of cost such as JupyterLab and Visual Studio Code, and select the one that works best for you. Important about these IDEs is that you don’t need necessarily internet connection to run them or to work with them. Check this entry to know more about the logic of [[Coding in Notebooks|coding in notebooks]]. |
| − | Anaconda distribution contains several free and paid IDEs that you can try out right awat. If you don’t want to use an IDE for now, you can also use a web application called “Google Colab”, which offers a development environment in the notebooks format. If your computer is not powerful enough for some data science tasks, you can use Google Colab and either use it for free and pay for extra computational power if needed (for example purchasing some GPU's). However, you need a stable internet connection for this. Check this entry to [[Getting started with Google Colab|get started with Google Colab]]. | + | Anaconda distribution contains several free and paid IDEs that you can try out right awat. If you don’t want to use an IDE for now, you can also use a web application called “Google Colab”, which offers a development environment in the notebooks format. If your computer is not powerful enough for some data science tasks, you can use Google Colab and either use it for free and pay for extra computational power if needed (for example purchasing some GPU's). However, you need a stable internet connection for this. Check this entry to [[Getting started with Google Colab|get started with Google Colab]]. |
| − | == Jupyter Lab | + | == JupyterLab == |
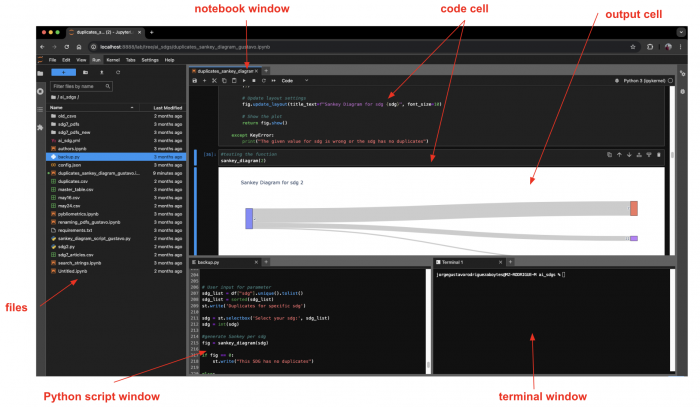
| − | Jupyter Lab | + | JupyterLab is an evolution of a Jupyter Notebook, both created as part of the non-profit and open-source Jupyter Project. A Jupyter Notebbok is a coding environment where you can combine text/markdown cells with code cells and run the code cells independently instead of running the whole python script. Nonetheless, Jupyter Lab not only allows you to work with Jupyter Notebooks, but also with conventional python scripts, text and markdown files. In this interface you can also open and read excel files (both .xlsx and .csv) and pdfs, and have access directly to your computer's terminal. In the image below, you can see an example of JupyterLab interface. |
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Jupyterlab interface.png|700px|thumbnail|center|JupyterLab interface. Source: own]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | For installing Jupyter Lab, check the instructions on their [https://jupyter.org/install installation page]; however, there are no graphic user interface installers. You have to use the [[Learning to Use Computer's Terminal|terminal]] and use a [[Package Managers in Python|package manager]] (either pip or conda) to install it. | ||
== Visual Studio Code == | == Visual Studio Code == | ||
| − | |||
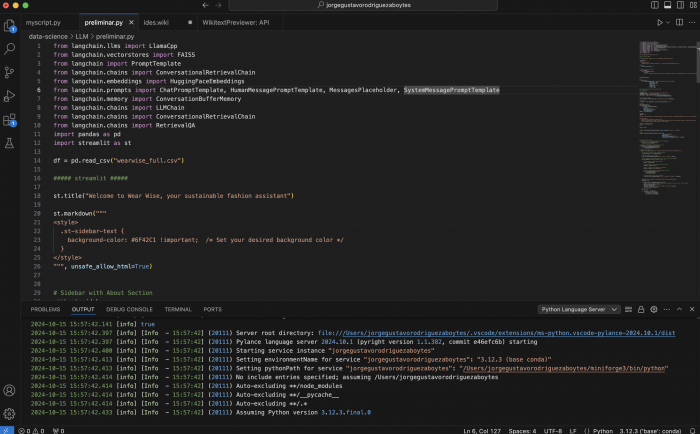
| − | == Other IDEs == | + | Visual Studio Code (VS Code) is a powerful and lightweight code editor |
| − | + | developed by Microsoft. It is designed to support a wide variety of | |
| + | programming languages, including Python, JavaScript, C++, and many more. | ||
| + | One of its core strengths is its highly customizable nature, allowing | ||
| + | users to extend its functionality with extensions available through | ||
| + | the integrated marketplace. For example, you can install Python-specific | ||
| + | tools to facilitate linting, debugging, and auto-completion, making it | ||
| + | an excellent choice for data analysis and scientific computing projects. | ||
| + | VS Code also integrates Git for version control, providing an intuitive | ||
| + | interface for committing changes, managing branches, and resolving | ||
| + | merge conflicts. The integrated terminal allows you to execute code | ||
| + | without leaving the editor, streamlining the development workflow. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Vsc inteface.png|700px|thumbnail|center|Example of a python script in Visual Studio Code. Source: own]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Beyond basic code editing, VS Code includes advanced features like | ||
| + | IntelliSense, which provides smart code completions based on variable | ||
| + | types and function definitions, making coding faster and less error-prone. | ||
| + | The built-in debugging tool allows you to set breakpoints, inspect variables, | ||
| + | and step through code execution, making it easier to identify and fix issues. | ||
| + | Additionally, VS Code supports Jupyter notebooks, enabling users to work | ||
| + | interactively on data science projects directly within the editor. This | ||
| + | feature is particularly useful when working on Python-based projects related | ||
| + | to machine learning, data visualization, or scientific computing. | ||
| + | |||
| + | VS Code offers a rich set of features that enhance the developer experience: | ||
| + | |||
| + | - **Syntax highlighting and code completion:** Provides color-coded syntax highlighting for different programming languages, making code easier to read and understand. Code completion suggests code snippets as you type, accelerating development. | ||
| + | - **Integrated terminal:** Eliminates the need to switch between separate terminal windows. You can run code, navigate your file system, and interact with the command line directly within VS Code. | ||
| + | - **Git integration:** Seamless integration with Git allows you to version control your code, track changes, and collaborate with others effectively. | ||
| + | - **Debugging tools:** Built-in debugging features enable you to step through code line by line, inspect variables, and identify errors efficiently. | ||
| + | - **Customization:** VS Code allows extensive customization through themes, keyboard shortcuts, and a vast marketplace of extensions. You can tailor the editor to your specific workflow and preferences | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Other IDEs = PyCharm Functionalities and Its Suitability for Data Analysis == | ||
| + | |||
| + | PyCharm, developed by JetBrains, is a full-featured Integrated Development Environment (IDE) designed specifically for Python development. It offers | ||
| + | a rich set of tools aimed at professional software developers, such as intelligent code completion, refactoring, and an advanced debugger. PyCharm | ||
| + | also integrates well with version control systems like Git, and its virtual | ||
| + | environment support makes managing dependencies straightforward. For Python | ||
| + | developers working on large-scale applications, its powerful capabilities | ||
| + | make it a leading choice. Its extensive plugin support allows users to | ||
| + | enhance its functionality, including adding tools for scientific computing, | ||
| + | Django for web development, and more. The built-in testing frameworks, | ||
| + | database tools, and profilers make PyCharm an all-encompassing IDE for | ||
| + | software engineering tasks. | ||
| + | |||
| + | However, PyCharm may not be the most optimal tool for data analysis, especially compared to more lightweight environments like Visual Studio Code or Jupyter Notebook. PyCharm's relatively heavier memory usage can | ||
| + | slow down workflows, particularly when working with large datasets, which is common in data analysis. Additionally, while PyCharm offers scientific mode and supports Jupyter notebooks, its setup is more complex, and the | ||
| + | interface can feel overwhelming to users focused on exploratory data analysis or quick prototyping. For those primarily working in machine learning, | ||
| + | data visualization, or experimentation with Python, the overhead of PyCharm’s advanced features can be a distraction, making more streamlined tools like Jupyter or VS Code a better fit for data analysis projects. | ||
Latest revision as of 14:17, 15 October 2024
Still in Edition Mode
Contents
What is an IDE?
You have installed Python and its distribution or package manager, now what? The next important question is where are you going to write and run your Python code?
You can basically write Python code in any text editor applications such as Windows Notepad or macOS TextEdit, and then run it in your terminal command line (Windows Powershell or macOS terminal). For example, you can a create a very short python script:
name = "gustavo"
print("Hello world! My name is " + name)
You save the text file as “myscript.py” and then run it in the terminal as follows:
(base) user91@mycomputer ~ % python myscript.py Hello world! My name is Gustavo
However, in very few exceptions people run python in this way. Normally, what is used is a Integrated Development Environment (IDE). These IDEs are applications where you can write and run Python code in an easier and more comfortable way. For example, this is the same python code but run in a Jupyter Notebook:
The difference between both are noticeable. Coding in an IDE provides several advantages or functionalities, for example, the text color. In the above Jupyter Notebook example, you can see that the variable name is in white, the string value is in red, the function print() is in green. This allows you to better identify the several components of your code. In this sense, working in an IDE helps you to better understand and read your code, and track errors. Depending on the IDE, you get different functionalities such as autocompletion, file management, version control, automation tools, visualization, etc.
Among the most popular IDEs are JupyterLab (which contains Jupyter Notebooks), Visual Studio, RStudio Code and PyCharm, however the latter is more dedicated for python web development. It is recommended to first try IDEs that are free of cost such as JupyterLab and Visual Studio Code, and select the one that works best for you. Important about these IDEs is that you don’t need necessarily internet connection to run them or to work with them. Check this entry to know more about the logic of coding in notebooks.
Anaconda distribution contains several free and paid IDEs that you can try out right awat. If you don’t want to use an IDE for now, you can also use a web application called “Google Colab”, which offers a development environment in the notebooks format. If your computer is not powerful enough for some data science tasks, you can use Google Colab and either use it for free and pay for extra computational power if needed (for example purchasing some GPU's). However, you need a stable internet connection for this. Check this entry to get started with Google Colab.
JupyterLab
JupyterLab is an evolution of a Jupyter Notebook, both created as part of the non-profit and open-source Jupyter Project. A Jupyter Notebbok is a coding environment where you can combine text/markdown cells with code cells and run the code cells independently instead of running the whole python script. Nonetheless, Jupyter Lab not only allows you to work with Jupyter Notebooks, but also with conventional python scripts, text and markdown files. In this interface you can also open and read excel files (both .xlsx and .csv) and pdfs, and have access directly to your computer's terminal. In the image below, you can see an example of JupyterLab interface.
For installing Jupyter Lab, check the instructions on their installation page; however, there are no graphic user interface installers. You have to use the terminal and use a package manager (either pip or conda) to install it.
Visual Studio Code
Visual Studio Code (VS Code) is a powerful and lightweight code editor developed by Microsoft. It is designed to support a wide variety of programming languages, including Python, JavaScript, C++, and many more. One of its core strengths is its highly customizable nature, allowing users to extend its functionality with extensions available through the integrated marketplace. For example, you can install Python-specific tools to facilitate linting, debugging, and auto-completion, making it an excellent choice for data analysis and scientific computing projects. VS Code also integrates Git for version control, providing an intuitive interface for committing changes, managing branches, and resolving merge conflicts. The integrated terminal allows you to execute code without leaving the editor, streamlining the development workflow.
Beyond basic code editing, VS Code includes advanced features like IntelliSense, which provides smart code completions based on variable types and function definitions, making coding faster and less error-prone. The built-in debugging tool allows you to set breakpoints, inspect variables, and step through code execution, making it easier to identify and fix issues. Additionally, VS Code supports Jupyter notebooks, enabling users to work interactively on data science projects directly within the editor. This feature is particularly useful when working on Python-based projects related to machine learning, data visualization, or scientific computing.
VS Code offers a rich set of features that enhance the developer experience:
- **Syntax highlighting and code completion:** Provides color-coded syntax highlighting for different programming languages, making code easier to read and understand. Code completion suggests code snippets as you type, accelerating development. - **Integrated terminal:** Eliminates the need to switch between separate terminal windows. You can run code, navigate your file system, and interact with the command line directly within VS Code. - **Git integration:** Seamless integration with Git allows you to version control your code, track changes, and collaborate with others effectively. - **Debugging tools:** Built-in debugging features enable you to step through code line by line, inspect variables, and identify errors efficiently. - **Customization:** VS Code allows extensive customization through themes, keyboard shortcuts, and a vast marketplace of extensions. You can tailor the editor to your specific workflow and preferences
Other IDEs = PyCharm Functionalities and Its Suitability for Data Analysis
PyCharm, developed by JetBrains, is a full-featured Integrated Development Environment (IDE) designed specifically for Python development. It offers a rich set of tools aimed at professional software developers, such as intelligent code completion, refactoring, and an advanced debugger. PyCharm also integrates well with version control systems like Git, and its virtual environment support makes managing dependencies straightforward. For Python developers working on large-scale applications, its powerful capabilities make it a leading choice. Its extensive plugin support allows users to enhance its functionality, including adding tools for scientific computing, Django for web development, and more. The built-in testing frameworks, database tools, and profilers make PyCharm an all-encompassing IDE for software engineering tasks.
However, PyCharm may not be the most optimal tool for data analysis, especially compared to more lightweight environments like Visual Studio Code or Jupyter Notebook. PyCharm's relatively heavier memory usage can slow down workflows, particularly when working with large datasets, which is common in data analysis. Additionally, while PyCharm offers scientific mode and supports Jupyter notebooks, its setup is more complex, and the interface can feel overwhelming to users focused on exploratory data analysis or quick prototyping. For those primarily working in machine learning, data visualization, or experimentation with Python, the overhead of PyCharm’s advanced features can be a distraction, making more streamlined tools like Jupyter or VS Code a better fit for data analysis projects.