Difference between revisions of "Sustainability Methods:About"
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
<br/><br/> | <br/><br/> | ||
* [[:Category:Quantitative|Quantitative]] - [[:Category:Qualitative|Qualitative]] | * [[:Category:Quantitative|Quantitative]] - [[:Category:Qualitative|Qualitative]] | ||
| − | + | <br/> | |
* [[:Category:Inductive|Inductive]] - [[:Category:Deductive|Deductive]] | * [[:Category:Inductive|Inductive]] - [[:Category:Deductive|Deductive]] | ||
| − | + | <br/> | |
* [[:Category:Individual|Individual]] - [[:Category:System|System]] - [[:Category:Global|Global]] | * [[:Category:Individual|Individual]] - [[:Category:System|System]] - [[:Category:Global|Global]] | ||
| − | + | <br/> | |
* [[:Category:Past|Past]] - [[:Category:Present|Present]] - [[:Category:Future|Future]] | * [[:Category:Past|Past]] - [[:Category:Present|Present]] - [[:Category:Future|Future]] | ||
| − | + | <br/> | |
You can click on each category for more information and all the entries that belong to this category | You can click on each category for more information and all the entries that belong to this category | ||
<br/><br/> | <br/><br/> | ||
Revision as of 11:31, 18 June 2020
About this wiki
The Sustainability Methods wiki ...
Scientific Methods
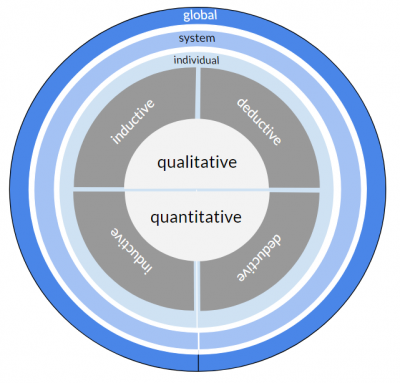
Each scientific method that is described on this Wiki has been categorized in the following categories:
- Individual - System - Global
You can click on each category for more information and all the entries that belong to this category
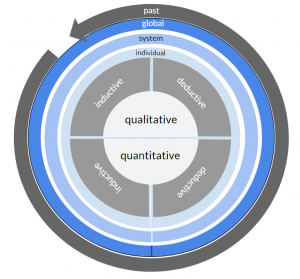
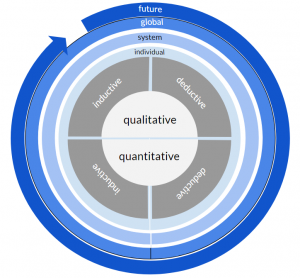
This visualisation refers to the majority of methods that focus on a slice of time - the present.
However, a range of methods exists that enable the researchers to investigate the past or the future. For these methods, the concept can be adapted to indicate a focus on the past (left) and a focus on the future (right).
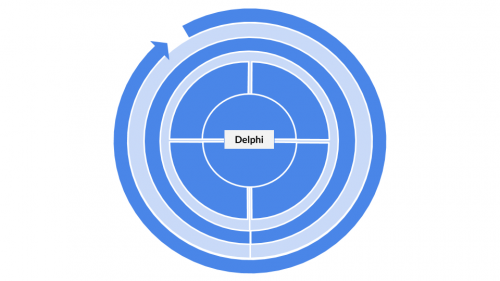
This visualisation enables us to characterize every method according to these categories. As an example, the Delphi method is both quantitative and qualitative, both inductive and deductive, looks at systems and into the future. The respective visualisation therefore looks like this: